Risk Management Process for A Transformation Program
This document outlines a comprehensive risk management process tailored for a Business Support Systems (BSS) transformation program within a telecommunications or IT company. It details the key steps involved in identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks throughout the program lifecycle, ensuring successful implementation and minimizing potential disruptions. The process emphasizes proactive risk management to enhance decision-making, improve project outcomes, and protect the organization’s strategic objectives.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
A BSS transformation program is a complex undertaking that involves significant changes to the systems and processes that support a telecom or IT company’s core business functions, such as customer management, billing, and order management. These programs are inherently risky due to their scale, complexity, and impact on critical business operations. Effective risk management is crucial for ensuring the program’s success and minimizing potential negative consequences.
2. Risk Management Framework
The risk management framework provides a structured approach to managing risks throughout the BSS transformation program. It consists of the following key elements:
- Risk Management Policy: A formal document that outlines the organization’s commitment to risk management, defines roles and responsibilities, and establishes the overall approach to risk management.
- Risk Management Plan: A detailed plan that describes how risk management will be implemented throughout the BSS transformation program. It includes specific procedures, tools, and techniques for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks.
- Risk Register: A central repository for documenting all identified risks, their assessments, mitigation plans, and monitoring activities.
- Risk Management Team: A dedicated team responsible for overseeing the risk management process, facilitating risk assessments, and monitoring the effectiveness of mitigation plans.
3. Risk Management Process
as part of Risk Management Process for A Transformation Program, the risk management process consists of the following steps:
3.1. Risk Identification
The first step is to identify potential risks that could impact the BSS transformation program. This involves brainstorming sessions, expert interviews, and reviews of project documentation, industry reports, and historical data. Check out: Project and PMO Governance in Jira – 15 Recommended Dashboard – Exceediance
Techniques for Risk Identification:
- Brainstorming: Gather stakeholders to generate a comprehensive list of potential risks.
- Checklists: Use predefined checklists based on past projects and industry best practices to identify common risks.
- Expert Interviews: Consult with subject matter experts to identify potential risks based on their experience and knowledge.
- SWOT Analysis: Analyze the program’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to identify potential risks.
- Lessons Learned: Review past projects to identify risks that occurred and how they were managed.
Categories of Risks:
- Technical Risks: Risks related to the technology being implemented, such as system integration issues, data migration challenges, and performance problems.
- Business Risks: Risks related to the business impact of the transformation, such as disruption to business operations, customer dissatisfaction, and revenue loss.
- Organizational Risks: Risks related to the organization’s ability to manage the transformation, such as lack of resources, inadequate skills, and resistance to change.
- Project Management Risks: Risks related to the management of the program, such as scope creep, schedule delays, and budget overruns.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Risks related to compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.

3.2. Risk Assessment
Once risks have been identified, they need to be assessed to determine their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This involves assigning a risk score based on the severity of the impact and the probability of the risk occurring.
Risk Assessment Matrix:
A risk assessment matrix is a tool used to prioritize risks based on their impact and likelihood. It typically consists of a table with impact levels (e.g., low, medium, high) on one axis and likelihood levels (e.g., low, medium, high) on the other axis. Each cell in the matrix represents a risk score, which is used to prioritize risks for mitigation.
Qualitative Risk Assessment:
Qualitative risk assessment involves using subjective judgment to assess the impact and likelihood of risks. This is typically done through expert interviews and group discussions.
Quantitative Risk Assessment:
Quantitative risk assessment involves using numerical data to assess the impact and likelihood of risks. This may involve using statistical analysis, simulation models, or other quantitative techniques.
3.3. Risk Mitigation
In the Risk Management Process for A Transformation Program, after assessing the risks, mitigation plans need to be developed to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risks. This involves identifying specific actions that can be taken to prevent the risk from occurring or to minimize its impact if it does occur.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Avoidance: Eliminate the risk altogether by changing the project plan or scope.
- Transference: Transfer the risk to a third party, such as an insurance company or a vendor.
- Mitigation: Reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk by implementing specific controls or actions.
- Acceptance: Accept the risk and take no action, typically for low-impact, low-likelihood risks.

Developing Mitigation Plans:
Mitigation plans should include the following elements:
- Risk Description: A clear description of the risk being mitigated.
- Mitigation Actions: Specific actions that will be taken to mitigate the risk.
- Responsible Party: The individual or team responsible for implementing the mitigation actions.
- Timeline: The timeframe for completing the mitigation actions.
- Resources: The resources required to implement the mitigation actions.
- Contingency Plan: A plan for what to do if the mitigation actions are not successful.

3.4. Risk Monitoring and Control
The final step is to monitor the effectiveness of the mitigation plans and to control any changes to the risk profile. This involves regularly reviewing the risk register, tracking the progress of mitigation actions, and updating the risk assessment as needed.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
KPIs can be used to track the effectiveness of mitigation plans and to identify any emerging risks. Examples of KPIs include:
- Number of risks identified
- Number of risks mitigated
- Cost of risk mitigation
- Impact of risks that occurred
Regular Risk Reviews:
Regular risk reviews should be conducted to assess the overall risk profile of the BSS transformation program and to identify any new or emerging risks. These reviews should involve key stakeholders and should be documented in the risk register.
Change Management:
In Risk Management Process for A Transformation Program, Changes to the BSS transformation program can introduce new risks or alter the impact or likelihood of existing risks. Therefore, a robust change management process is essential to ensure that all changes are properly assessed for their potential impact on the risk profile.
4. Roles and Responsibilities
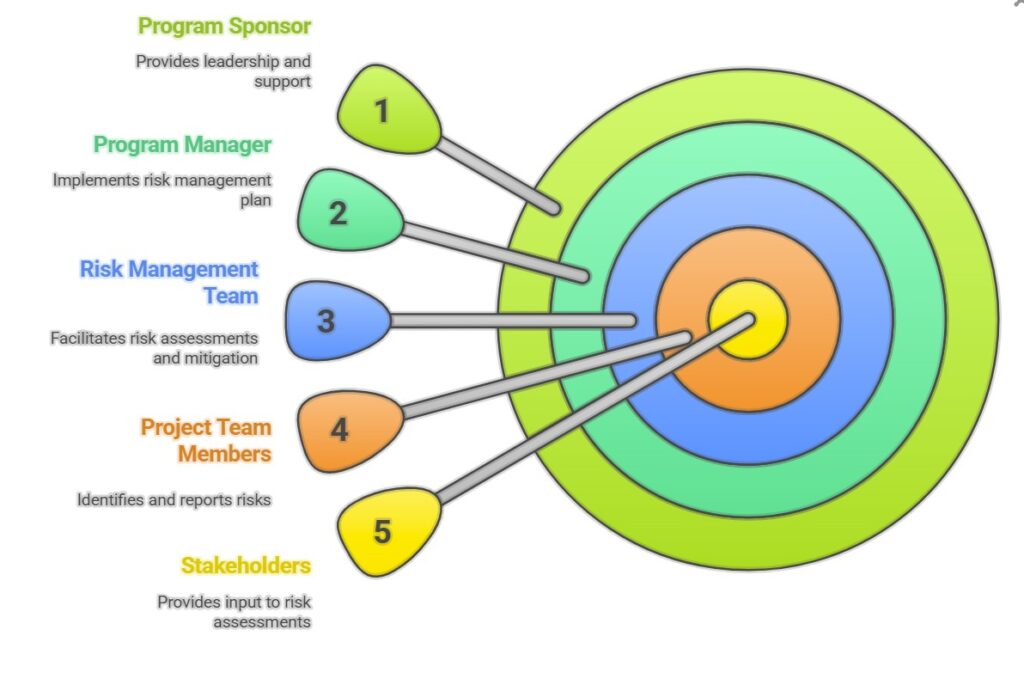
- Program Sponsor: Provides overall leadership and support for the risk management process.
- Program Manager: Responsible for implementing the risk management plan and ensuring that risks are effectively managed throughout the program lifecycle.
- Risk Management Team: Facilitates risk assessments, develops mitigation plans, and monitors the effectiveness of mitigation actions.
- Project Team Members: Responsible for identifying and reporting risks, and for implementing mitigation actions as assigned.
- Stakeholders: Provide input to the risk management process and participate in risk assessments.
5. Tools and Techniques
- Risk Register Software: A software tool for managing the risk register and tracking risk-related activities.
- Risk Assessment Templates: Standardized templates for documenting risk assessments and mitigation plans.
- Project Management Software: Software tools for managing project schedules, budgets, and resources, which can also be used to track risk-related activities.
- Communication Tools: Tools for communicating risk information to stakeholders, such as email, project websites, and regular status reports.
6. Conclusion
Effective risk management is essential for the success of a BSS transformation program. By implementing a structured risk management process, organizations can proactively identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks, minimizing potential disruptions and ensuring that the program achieves its objectives. This document provides a framework for developing and implementing a risk management process tailored to the specific needs of a BSS transformation program in a telecom or IT company. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of the risk management plan are crucial to address evolving risks and ensure the program’s success. Digital Transformation Risk Management: A Complete Guide
you may like these articles:
- 14 Top Skills Of a Successful Project Manager – Exceediance
- 46 Hilarious Phrases for Project Managers to Use in Meetings – Exceediance
- 50 Quick Proverbs For Project Managers To Improve Communication – Exceediance
