The Ultimate Guide to Google Tag Manager GTM
Whether you’re a marketer, analyst, or developer, understanding Google Tag Manager is a game-changer. This guide will take you from beginner to advanced levels with practical, free ways to start testing today. Let us start The Ultimate Guide to Google Tag Manager GTM
Table of Contents
What is Google Tag Manager
The Ultimate Guide to Google Tag Manager GTM. Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free tool that allows you to manage and deploy marketing tags (snippets of code or tracking pixels) on your website or mobile app without modifying the source code. Excellent Benefits of Google Analytics & How to Setup – Exceediance
As a business owner, tags help you understand what your visitors do on your website—like what pages they visit, which buttons they click, or if they make a purchase. This information shows you which ads are working and where your customers are coming from, so you can make better decisions and grow your business more effectively.
Benefits of Google Tag Manager (GTM)
- No Coding Needed: Add and manage marketing and tracking tools without editing your website’s code.
- Faster Tag Deployment: Launch new tags (like Google Analytics, ads, or Facebook Pixel) in minutes instead of waiting for a developer.
- Centralized Tag Control: Manage all your tracking codes from one dashboard instead of editing multiple pages.
- Error Reduction: Avoid mistakes in code by using GTM’s tag templates and preview features.
- Real-Time Testing: Use Preview Mode to test tags and triggers before publishing them live.
- Faster Website Updates: Make tracking changes quickly without needing to update your entire site.
- Supports All Tags: Add any kind of tracking script—Google Ads, Hotjar, LinkedIn, custom HTML, etc.
- Improved Site Speed: Helps reduce the number of scripts on your site, improving load time.
- Event Tracking: Track clicks, form submissions, scrolls, downloads, and more—without adding code.
- Affiliate Link Monitoring: See how often your affiliate links are clicked for better partner performance.
- Flexible Triggers: Set tags to fire only when certain conditions are met—like clicking a specific button or visiting a certain page.
- Version History: Keeps a full log of all changes so you can revert to earlier versions anytime.
- Built-In Debugging: Helps identify and fix tag issues using GTM’s built-in error detection tools.
- User Role Management: Assign different access levels to team members (e.g., editor, admin).
- Improved Data Accuracy: Ensures clean, consistent data is sent to platforms like Google Analytics.
- Supports GA4 & UA: Works with the latest Google Analytics 4 (GA4) as well as older versions.
- Easy Integration: Seamlessly connects with Google tools like Ads, Optimize, and Analytics.
- Secure Tag Execution: Reduces risk of malicious or broken code on your site through sandboxing.
- Boosts Marketing ROI: Helps marketing teams measure campaign effectiveness and improve targeting.
- Free to Use: GTM is a free tool with enterprise-grade features and no monthly cost.
Practical Example: How Google GTM Helps Your Business
If you have an online store that sells mobiles, laptops, monitors, keyboards, and mice, Google Tag Manager (GTM) can help your business in many ways. Here’s how, in simple language:
- Track What People Click
GTM can show you which products people click on the most—like if more people are interested in mobiles or laptops. - Know What’s Selling and What’s Not
You can set up tracking to see which products are being added to the cart, purchased, or ignored. This helps you know what’s popular and what needs better promotion. - See Where Customers Are Coming From
GTM can track if your visitors come from Google Ads, Facebook, Instagram, or email campaigns. This helps you invest your money where it’s working best. - Measure Ad Performance
You can use GTM to connect your store with tools like Google Ads or Facebook Pixel. It tells you which ad brought in a sale so you don’t waste money on ads that don’t work. - Improve Checkout Process
You can track if people are dropping off during checkout. If many people leave before buying, you know something needs fixing. - No Coding Needed Every Time
You don’t need to ask a developer every time you want to track something new. GTM lets you do it from one place without editing your website’s code.
In short:
Google Tag Manager helps you understand what’s happening on your store, which products are doing well, and where your customers come from—so you can make smarter decisions and grow your sales.
What Does GTM Do
- Centralizes all tracking codes: You can manage all your tracking in one place instead of adding separate codes for every tool, saving time and avoiding confusion.
- Fires tags based on user behavior or triggers such as clicks, pageviews, and scrolls: It automatically tracks what users do on your website—like clicking a button or visiting a page—so you know what’s working.
- Passes data to third-party platforms like GA4, Meta Ads, and others: It sends the right information to tools like Google Analytics or Facebook Ads, helping you understand your customers and improve marketing.
- Reduces code clutter on your website: You don’t need to add lots of tracking codes directly into your site, which keeps it clean and easier to maintain.
- Speeds up site deployment of marketing and tracking tools: You can quickly set up or change tracking without waiting for a developer, helping you move faster with your marketing plans.
Core Concepts and Modules
1. Tags
These are snippets of code that send information to third-party tools. Examples include:
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
- Facebook Pixel
- LinkedIn Insight Tag
- Google Ads Conversion Tracking
- Custom HTML or JavaScript
2. Triggers
Triggers tell GTM when to fire a tag. Examples include:
- Page Load (All Pages)
- Clicks on a button or link
- Form Submission
- Scroll Depth
- Custom Events
3. Variables
Variables are placeholders used in triggers and tags.
- Built-in Variables (such as Page URL, Click Classes)
- User-defined Variables (such as JavaScript Variables, Data Layer Variables)
4. Data Layer
A structured JavaScript object that stores data you want GTM to use.
Example:
javascriptCopyEditwindow.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
window.dataLayer.push({
'event': 'purchase',
'transactionId': '12345',
'transactionTotal': '49.99'
});
5. Containers
Each website or app has its own container where you manage all tags, triggers, and variables.
Why Use GTM
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | Add and update tracking without touching code |
| Speed | Deploy tags quickly across all pages |
| Control | Central dashboard to manage all scripts |
| Version Control | Built-in versioning and rollback features |
| Security | Permissions and workspaces for collaboration |
| Cost | Free of charge for most use cases |
Real-World Examples
- Track button clicks for sign-ups
- Send scroll-depth data to GA4
- Trigger Facebook events only on specific pages
- Track YouTube video plays
- Fire LinkedIn tags after a form submission
Getting Started: Free Practice Setup
Can I Practice Without Spending Money?
Yes. Here’s how:
- Create a Free Google Tag Manager Account
Visit tagmanager.google.com and sign up. - Use a Free Test Website
Options include GitHub Pages, Netlify, or installing GTM on your personal WordPress blog. - Use GTM Preview Mode or Tag Assistant
These tools allow full testing without needing live traffic.
Visit tagmanager.google.com and Sign up, below page will appear. In the container name enter your website name
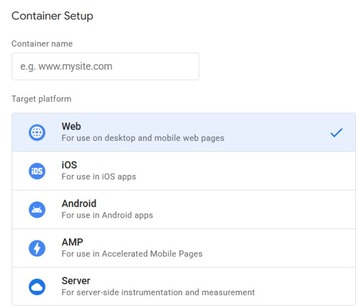
Once you fill in, you will get a code similar to below snapshot. Search for your GTM ID that should be something like GTM-XXXXXXXX . Not it down, this is your GTM ID.

Now in your WordPress plugin section, search for the below plugin
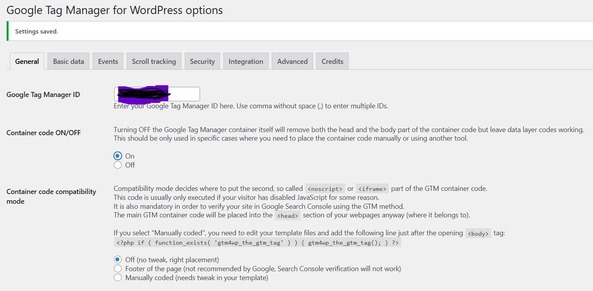
Once you install and activate, you will see below page, enter your GTM and enable Container code ON/OFF to On, as shown below
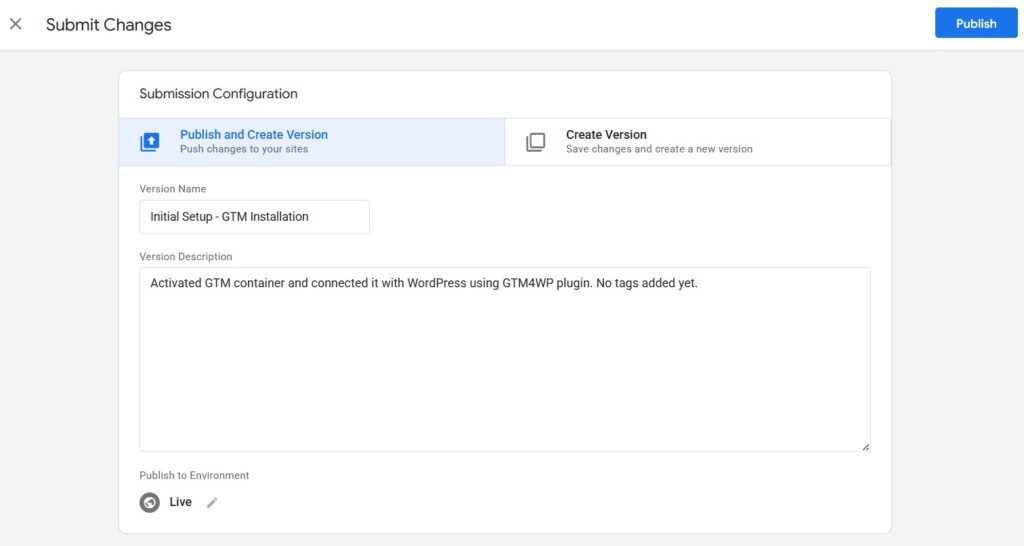
Now go to Google Tag Manager and enter following information:
1. Version Name
Enter something simple and clear like:Initial Setup - GTM Installation
2. Version Description
Describe what this version includes. Example:Activated GTM container and connected it with WordPress using GTM4WP plugin. No tags added yet.
3. Make Sure “Publish and Create Version” is Selected
This will both publish your changes and create a version for reference or rollback later.
4. Ensure “Publish to Environment” is Set to Live
It is already showing as “Live” in your screenshot, which is perfect.
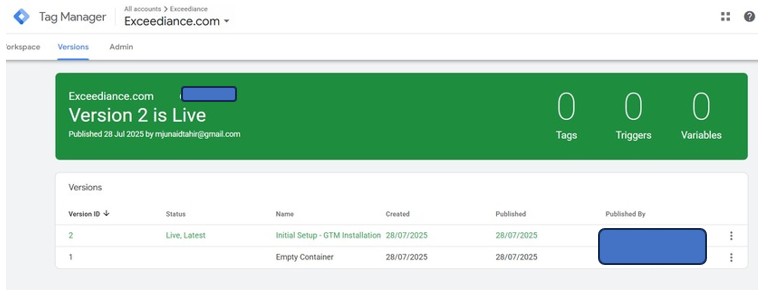
5. Click the Blue “Publish” Button in the Top Right
Once you do this, your container is officially live and running on your website.
Here’s How to Use Google Tag Assistant (Preview Mode)
Step 1: Visit Tag Assistant
Go to this link:
https://tagassistant.google.com/
Step 2: Click Start
Step 3: Enter your website URL (e.g., https://exceediance.com)
Then click Connect
This will open your site in a new browser tab.
Step 4: Interact with Your Website
Click a few pages, buttons, scroll, etc.
Step 5: Go back to the Tag Assistant tab
You should now see:
- Your GTM container ID
- Any tags that fired (if you have added any)
- A list of triggered events, e.g., Page View
Step-by-Step: Setting Up Your First Tag
Let’s walk through setting up Google Analytics 4 (GA4) via GTM.
Step 1: Create a Container
Go to GTM > New Account > Enter Website Name > Create Container (Web)
Step 2: Add GA4 Tag
- Go to Tags > New > Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration
- Enter your Measurement ID from GA4
- Set the trigger to All Pages
Step 3: Preview and Test
- Click Preview
- Enter your website URL
- Open your site in a new tab; the GTM Debug panel will show tag activity
Step 4: Publish
- Once testing is complete, click Submit and publish your container
Intermediate to Advanced GTM Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom HTML Tags | Add custom JavaScript, schema, or third-party integrations |
| Lookup Tables | Dynamically set values like environment-specific tracking IDs |
| JavaScript Regex | Build advanced triggers using regular expressions |
| Auto-Event Tracking | Track clicks and forms without assigning IDs or classes manually |
| Data Layer Push | Push structured data like revenue, transaction ID, product details |
| Server-Side GTM | An alternative to client-side tagging for improved security and speed |
Common Use Cases and Automation Ideas
- Event-Based Goals: Track downloads, video views, or scroll interactions
- Marketing Automation: Trigger remarketing pixels after specific actions
- Form Analytics: Capture partial entries and drop-off points
- Enhanced eCommerce: Monitor product views, cart adds, and purchases
- Cross-Domain Tracking: Follow users across multiple websites
- Consent Management: Integrate tools like Cookiebot for GDPR compliance
Best Free Resources to Learn GTM
| Resource | Format | Access |
|---|---|---|
| Google Tag Manager Fundamentals | Online Course | Learning Google Tag Manager | LinkedIn Learning |
| MeasureSchool YouTube Channel | Videos and Tutorials | YouTube – Search “MeasureSchool GTM” |
| Analytics Mania | Tutorials and Templates | www.analyticsmania.com |
| Simo Ahava’s Blog | Advanced Techniques | www.simoahava.com |
| Tag Assistant Extension | Debug Tool | Chrome Extension Store |
Conclusion and Pro Tips
Learning GTM can be a transformative step in your data and digital marketing journey. It offers control, efficiency, and scalability—all without requiring deep coding skills. GTM Official certification or course : r/GoogleTagManager
Pro Tips
- Always test in Preview Mode before publishing
- Establish naming conventions for clarity and maintenance
- Use separate workspaces when collaborating on teams
- Combine GTM with Google Analytics 4 and Looker Studio for full insight
- Practice in a sandbox before going live
